深度模型Wide&Deep模型
00 序言
1、 记忆能力(memorization):模型直接根据历史数据中item或特征与特征之间出现的频次学习出item或特征之间的关联关系。
Memorization can be loosely defined as learning the frequent co-occurrence of items or features and exploiting the correlation available in the historical data.
简而言之,如果在历史数据中发现用户点击过item A和点击item B在样本中总是频繁成对出现,那么点击item A和点击item B就存在很强的关联关系,对于item B的点击率预估中,如果历史行为有点击item A,那么点击item B的点击率就很高。
广义线性模型LR模型具有很强的记忆能力。
2、 泛化能力(generalization):模型根据特征之间的相关性,探索过去从未或很少出现的新特征组合。
Generalization, on the other hand, is based on transitivity of correlation and explores new feature combinations that have never or rarely occurred in the past.
深度神经网络可以通过特征的多次自动组合,可以深度挖掘出一些新的特征组合,所以深度神经网络具有泛化能力
01 Wide&Deep模型结构
Wide&Deep模型的主要思路就是对LR模型具有的记忆能力和DNN模型具有的泛化能力进行组合,使得模型能够快速处理并记忆大量的历史行为特征,并具有很好的泛化能力。Wide&Deep模型结构如图所示
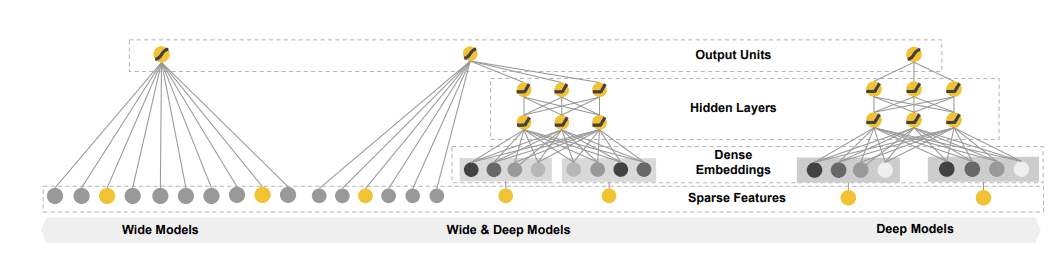
1、Wide部分
Wide侧的模型结构是一个线性模型LR模型$y=w^T x + b$,Wide侧的输入$x$是由原始特征和明文交叉特征组成,明文交叉特征通常通过原始特征的向量进行cross-product来实现的,具体公式为 \(\begin{aligned} \phi_k (x) = \prod_{i=1}^{d} x_{i}^{c_{ki}} \quad c_{ki}\in \{0, 1\} \end{aligned}\)
2、Deep部分
Deep侧的模型结构是常见的Embedding+DNN的模型,输入的ID类特征经过Embedding层得到每个特征的向量,然后Concat所有的向量,将Concat的向量再作为DNN的输入。
3、Wide&Deep模型输出
Wide&Deep模型最后的输出由Wide侧的输出加上Deep侧的输出作为模型的输出,即 \(\begin{aligned} y=sigmoid (w_{wide}y_{wide} + w_{deep} y_{deep} + b) \end{aligned}\)
4、Wide&Deep模型联合训练
Wide&Deep模型训练方式采用的是联合训练,直接在训练阶段就同时训练两部分的网络参数,在训练的过程中,Wide部分主要采用带L1正则的FTRL算法进行优化,Deep部分采用AdaGrad进行优化。 这种联合训练的方式有两个好处:一方面联合训练同时训练两部分网络的参数更有利于整体的最优化;另一方面联合训练可以有效降低整个网络的大小。
02 Wide&Deep模型的优缺点
- 优点:兼具记忆能力和泛化能力。
- 缺点:Wide部分仍需要人工进行特征组合的筛选。
03 Wide&Deep模型实现
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Embedding, Dense, Concatenate, Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
class WideDeepModel(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, feature_dim, embedding_dim, hidden_units):
super(WideDeepModel, self).__init__()
# Wide Component
self.wide_layer = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
# Deep Component
self.embedding_layer = Embedding(input_dim=feature_dim, output_dim=embedding_dim)
self.flatten = Flatten()
self.dense_layers = [Dense(units, activation='relu') for units in hidden_units]
# Concatenate Wide and Deep
self.concat = Concatenate()
# Output Layer
self.output_layer = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, inputs):
# Input Layer
input_layer = Input(shape=(inputs,))
# Wide Component
wide_output = self.wide_layer(input_layer)
# Deep Component
embedding_output = self.embedding_layer(input_layer)
deep_output = self.flatten(embedding_output)
for dense_layer in self.dense_layers:
deep_output = dense_layer(deep_output)
# Concatenate Wide and Deep
concat_output = self.concat([wide_output, deep_output])
# Output Layer
output = self.output_layer(concat_output)
return output